Serializando Dados
Quando falamos sobre serialização, estamos nos referindo tanto à serialização quanto à desserialização de dados.
A serialização entra em jogo em alguns pontos ao longo do ciclo de vida dos programas e das contas de programas da Solana:
- Serializando dados de instruções no cliente
- Desserializando dados de instruções no programa
- Serializando dados de contas no programa
- Desserializando dados de contas no cliente
É importante que as ações acima sejam suportadas pela mesma abordagem de serialização. Os trechos incluídos demonstram a serialização usando o Borsh.
Os exemplos apresentados neste documento são trechos extraídos do Modelo de Programa da CLI da Solana
Configurando a Serialização com o Borsh
As bibliotecas para o Borsh devem ser configuradas para o programa Rust, cliente Rust, cliente Node e/ou Python.
[package]
name = "solana-cli-template-program-bpf"
version = "0.1.0"
edition = "2018"
license = "WTFPL"
# See more keys and their definitions at https://doc.rust-lang.org/cargo/reference/manifest.html
[features]
no-entrypoint = []
[dependencies]
borsh = "0.9.0"
lazy_static = "1.4.0"
num-derive = "0.3"
num_enum = "0.5.1"
num-integer = "0.1.44"
num-traits = "0.2"
sol-template-shared = {path = "../shared"}
solana-program = "1.8.2"
thiserror = "1.0"
[dev-dependencies]
solana-program-test = "1.8.2"
solana-sdk = "1.8.2"
[lib]
crate-type = ["cdylib", "lib"]
[package]
name = "cli-program-template"
version = "0.1.5"
edition = "2018"
license = "WTFPL"
publish = false
[dependencies]
borsh = "0.9.0"
clap = "2.33.3"
lazy_static = "1.4.0"
serde = { version = "1.0.125", features = ["derive"] }
serde_yaml = "0.8.17"
sol-template-shared = {path = "shared"}
solana-clap-utils = "1.8.2"
solana-cli-config = "1.8.2"
solana-client = "1.8.2"
solana-logger = "1.8.2"
solana-remote-wallet = "1.8.2"
solana-sdk = "1.8.2"
tokio = { version = "1", features = ["full"] }
[workspace]
members = [
"program",
"shared",
]
[dev-dependencies]
lazy_static = "1.4.0"
solana-validator = "1.8.2"
solana-streamer = "1.8.2"
{
"name": "ts-program-template",
"version": "0.1.0",
"description": "Sample TS App",
"main": "client/nmain.ts",
"author": "",
"keywords": [],
"workspace": "client/",
"repository": {
"type": "git",
"url": "https: //github.com/hashblock/solana-cli-program-template"
},
"homepage": "https: //github.com/hashblock/solana-cli-program-template",
"scripts": {
"test:all": "npm run build:client && npm run test:client",
"build:client": "rm -rf ./.dist/client && tsc ",
"start": "node ./node_modules/.bin/mocha .dist/client/main.js",
"test:client": "npm run start",
"lint": "eslint --ext .ts client/* && prettier --check \"client/**/*.ts\"",
"lint:fix": "eslint --ext .ts client/* --fix",
"pretty": "prettier --write '{,client/**/}*.ts'"
},
"devDependencies": {
"@tsconfig/recommended": "^1.0.1",
"@types/chai": "^4.3.0",
"@types/eslint": "^7.28.2",
"@types/eslint-plugin-prettier": "^3.1.0",
"@types/mkdirp": "^1.0.2",
"@types/mocha": "^9.0.0",
"@types/prettier": "^2.4.1",
"@typescript-eslint/eslint-plugin": "^5.6.0",
"@typescript-eslint/parser": "^5.6.0",
"chai": "^4.3.4",
"eslint": "^8.2.0",
"eslint-config-google": "^0.14.0",
"eslint-config-prettier": "^8.3.0",
"eslint-plugin-prettier": "^4.0.0",
"html-webpack-plugin": "^5.5.0",
"mocha": "^9.1.3",
"prettier": "^2.4.1",
"start-server-and-test": "^1.14.0",
"ts-node": "^10.4.0",
"typescript": "^4.5.2"
},
"dependencies": {
"@solana/web3.js": "^1.31.0",
"borsh": "^0.7.0",
"env": "^0.0.2",
"fs": "^0.0.1-security",
"mkdirp": "^1.0.4",
"npm-check-updates": "^12.0.3",
"sync-request": "^6.1.0",
"update": "^0.4.2"
}
}
borsh-construct==0.1.0
solana==0.20.0
Como serializar dados de instrução no cliente
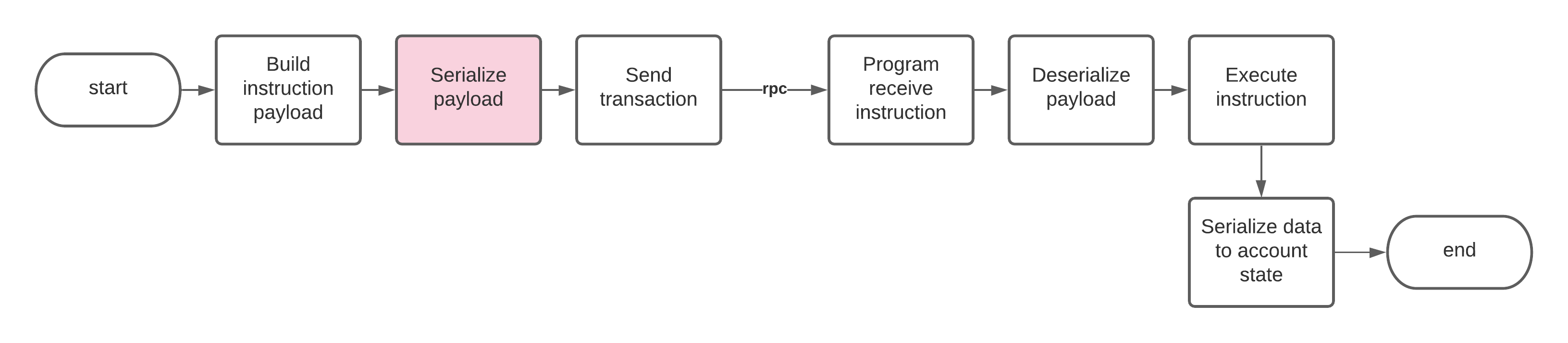
Se você estiver serializando dados de instrução de saída para enviar a um programa, ele deve espelhar como o programa desserializa os dados de instrução de entrada.
Neste modelo, um bloco de dados de instrução é um array serializado contendo, com exemplos:
| Instrução (Índice Variante) | Chave Serializada | Valor Serializado |
|---|---|---|
| Initialize (0) | não aplicável para instrução | não aplicável para instrução |
| Mint (1) | "foo" | "bar" |
| Transfer (2) | "foo" | não aplicável para instrução |
| Burn (2) | "foo" | não aplicável para instrução |
No exemplo a seguir, assumimos que a conta de propriedade do programa foi inicializada
// Include borsh functionality
import { serialize, deserialize, deserializeUnchecked } from "borsh";
import { Buffer } from "buffer";
// Get Solana
import {
Keypair,
Connection,
PublicKey,
Transaction,
TransactionInstruction,
sendAndConfirmTransaction,
} from "@solana/web3.js";
// Flexible class that takes properties and imbues them
// to the object instance
class Assignable {
constructor(properties) {
Object.keys(properties).map((key) => {
return (this[key] = properties[key]);
});
}
}
// Our instruction payload vocabulary
class Payload extends Assignable {}
// Borsh needs a schema describing the payload
const payloadSchema = new Map([
[
Payload,
{
kind: "struct",
fields: [
["id", "u8"],
["key", "string"],
["value", "string"],
],
},
],
]);
// Instruction variant indexes
enum InstructionVariant {
InitializeAccount = 0,
MintKeypair,
TransferKeypair,
BurnKeypair,
}
/**
* Mint a key value pair to account
* @param {Connection} connection - Solana RPC connection
* @param {PublicKey} progId - Sample Program public key
* @param {PublicKey} account - Target program owned account for Mint
* @param {Keypair} wallet - Wallet for signing and payment
* @param {string} mintKey - The key being minted key
* @param {string} mintValue - The value being minted
* @return {Promise<Keypair>} - Keypair
*/
export async function mintKV(
connection: Connection,
progId: PublicKey,
account: PublicKey,
wallet: Keypair,
mintKey: string,
mintValue: string
): Promise<string> {
// Construct the payload
const mint = new Payload({
id: InstructionVariant.MintKeypair,
key: mintKey, // 'ts key'
value: mintValue, // 'ts first value'
});
// Serialize the payload
const mintSerBuf = Buffer.from(serialize(payloadSchema, mint));
// console.log(mintSerBuf)
// => <Buffer 01 06 00 00 00 74 73 20 6b 65 79 0e 00 00 00 74 73 20 66 69 72 73 74 20 76 61 6c 75 65>
// let mintPayloadCopy = deserialize(schema, Payload, mintSerBuf)
// console.log(mintPayloadCopy)
// => Payload { id: 1, key: 'ts key', value: 'ts first value' }
// Create Solana Instruction
const instruction = new TransactionInstruction({
data: mintSerBuf,
keys: [
{ pubkey: account, isSigner: false, isWritable: true },
{ pubkey: wallet.publicKey, isSigner: false, isWritable: false },
],
programId: progId,
});
// Send Solana Transaction
const transactionSignature = await sendAndConfirmTransaction(
connection,
new Transaction().add(instruction),
[wallet],
{
commitment: "singleGossip",
preflightCommitment: "singleGossip",
}
);
console.log("Signature = ", transactionSignature);
return transactionSignature;
}
from borsh_construct import String, CStruct, U8
from enum import IntEnum
from solana.transaction import Transaction
from solders.pubkey import Pubkey
from solders.keypair import Keypair
from solders.instruction import Instruction, AccountMeta
from solders.rpc.responses import SendTransactionResp
from solana.rpc.api import Client
# Instruction variants for target program
class InstructionVariant(IntEnum):
INITIALIZE = 0
MINT = 1
TRANSFER = 2
BURN = 3
# Schema for sending instructionVariants to on-chain sample program
payload_schema = CStruct("id" / U8, "key" / String, "value" / String)
def construct_payload(instruction_variant: InstructionVariant, key: str, value: str):
"""Generate a serialized instructionVariant"""
return payload_schema.build({"id": instruction_variant, "key": key, "value": value})
def mint_kv(
client: Client,
program_pk: Pubkey,
account_pk: Pubkey,
wallet_kp: Keypair,
mint_key: str,
mint_value: str,
) -> SendTransactionResp:
"""Mint with a key/value pair to an account"""
# Construct the program payload for Mint invariant
payload_ser = construct_payload(InstructionVariant.MINT, mint_key, mint_value)
# print(payload_ser)
# => b'\x01\n\x00\x00\x00python key\x0c\x00\x00\x00python value'
# mint_payload_copy = payload_schema.parse(payload_ser)
# print(mint_payload_copy)
# => Container:
# => initialized = 1
# => key = u'python key' (total 10)
# => value = u'python value' (total 12)
# Construct the transaction with instructionVariant
txn = Transaction().add(
Instruction(
accounts=[AccountMeta(account_pk, False, True)], program_id=program_pk, data=payload_ser
)
)
return client.send_transaction(txn, wallet_kp)
# => {'jsonrpc': '2.0', 'result': '4ZdpWNdovdVaLextWSiqEBWp67k9rNTTUaX3qviHDXWY9c98bVtaRt5sasPhYzMVXHqhex78gzNKytcBnVH5CSTZ', 'id': 2}
/// Instruction payload gets serialized
#[derive(BorshSerialize)]
pub struct Payload<'a> {
variant: u8,
key: &'a str,
value: &'a str,
}
/// Perform a mint transaction consisting of a key/value pair
/// See submit_transaction below
pub fn mint_transaction(
rpc_client: &RpcClient,
accounts: &[AccountMeta],
wallet_signer: &dyn Signer,
mint_key: &str,
mint_value: &str,
mint_instruction_id: u8,
commitment_config: CommitmentConfig,
) -> Result<Signature, Box<dyn std::error::Error>> {
// Setup the payload. `mint_instruction_id` is instruction variant index = 1
let data = Payload<`_> {
variant: mint_instruction_id,
key: mint_key,
value: mint_value,
};
let instruction = Instruction::new_with_borsh(PROG_KEY.pubkey(), &data, accounts.to_vec());
submit_transaction(rpc_client, wallet_signer, instruction, commitment_config)
}
/// Submits the program instruction as per the
/// instruction definition
pub fn submit_transaction(
rpc_client: &RpcClient,
wallet_signer: &dyn Signer,
instruction: Instruction,
commitment_config: CommitmentConfig,
) -> Result<Signature, Box<dyn std::error::Error>> {
let mut transaction =
Transaction::new_unsigned(Message::new(&[instruction], Some(&wallet_signer.pubkey())));
let (recent_blockhash, _fee_calculator) = rpc_client
.get_recent_blockhash()
.map_err(|err| format!("error: unable to get recent blockhash: {}", err))?;
transaction
.try_sign(&vec![wallet_signer], recent_blockhash)
.map_err(|err| format!("error: failed to sign transaction: {}", err))?;
let signature = rpc_client
.send_and_confirm_transaction_with_spinner_and_commitment(&transaction, commitment_config)
.map_err(|err| format!("error: send transaction: {}", err))?;
Ok(signature)
}
Como desserializar dados de instrução no programa
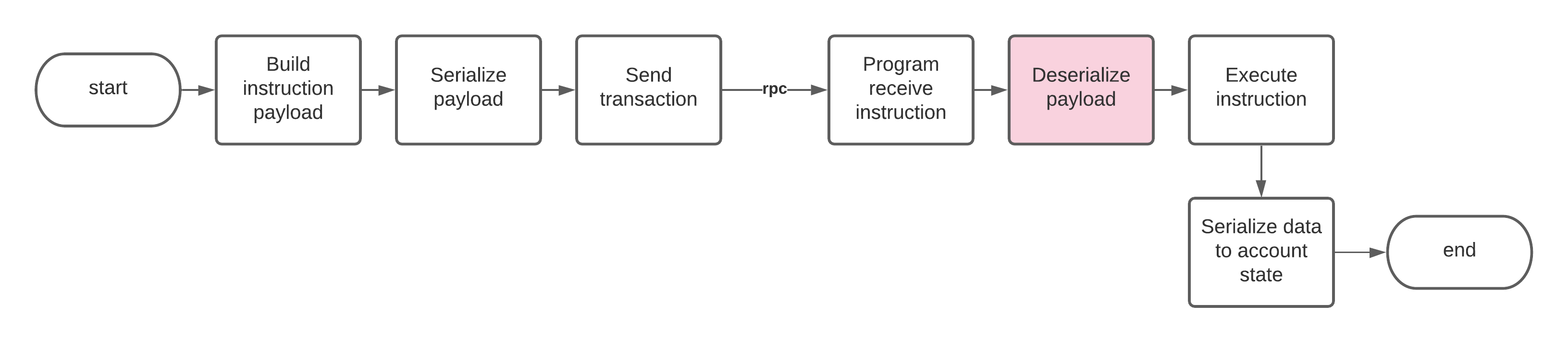
//! instruction Contains the main ProgramInstruction enum
use {
crate::error::SampleError, borsh::BorshDeserialize, solana_program::program_error::ProgramError,
};
#[derive(Debug, PartialEq)]
/// All custom program instructions
pub enum ProgramInstruction {
InitializeAccount,
MintToAccount { key: String, value: String },
TransferBetweenAccounts { key: String },
BurnFromAccount { key: String },
MintToAccountWithFee { key: String, value: String },
TransferBetweenAccountsWithFee { key: String },
BurnFromAccountWithFee { key: String },
}
/// Generic Payload Deserialization
#[derive(BorshDeserialize, Debug)]
struct Payload {
variant: u8,
arg1: String,
arg2: String,
}
impl ProgramInstruction {
/// Unpack inbound buffer to associated Instruction
/// The expected format for input is a Borsh serialized vector
pub fn unpack(input: &[u8]) -> Result<Self, ProgramError> {
let payload = Payload::try_from_slice(input).unwrap();
match payload.variant {
0 => Ok(ProgramInstruction::InitializeAccount),
1 => Ok(Self::MintToAccount {
key: payload.arg1,
value: payload.arg2,
}),
2 => Ok(Self::TransferBetweenAccounts { key: payload.arg1 }),
3 => Ok(Self::BurnFromAccount { key: payload.arg1 }),
4 => Ok(Self::MintToAccountWithFee {
key: payload.arg1,
value: payload.arg2,
}),
5 => Ok(Self::TransferBetweenAccountsWithFee { key: payload.arg1 }),
6 => Ok(Self::BurnFromAccountWithFee { key: payload.arg1 }),
_ => Err(SampleError::DeserializationFailure.into()),
}
}
}
Como serializar os dados da conta no programa
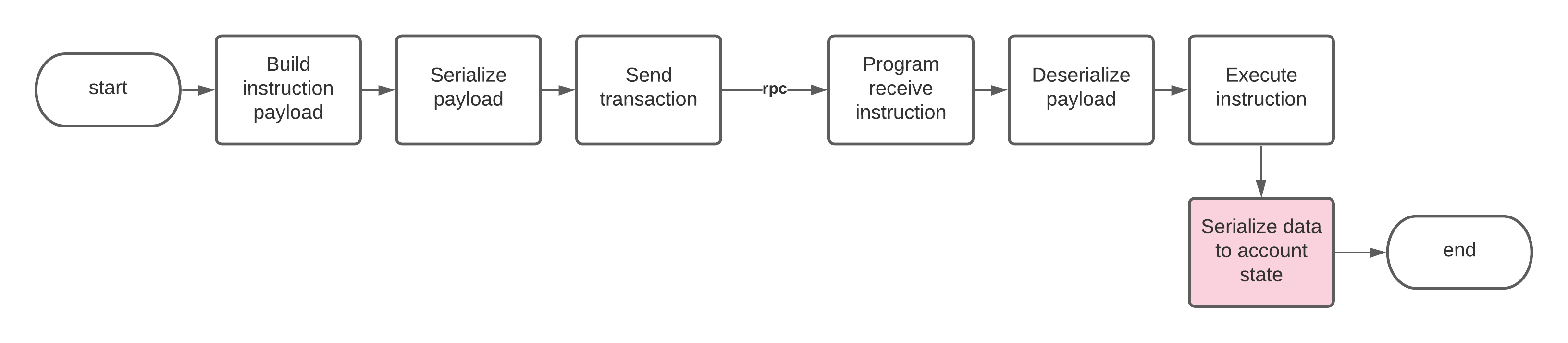
O bloco de dados da conta do programa (do repositório de amostra) é apresentado como
| Byte 0 | Bytes 1-4 | Bytes restantes até 1019 |
|---|---|---|
| Flag de inicialização | comprimento do BTreeMap serializado | BTreeMap (onde os pares chave-valor são armazenados) |
Pack
Uma palavra sobre o trait Pack
O trait Pack facilita a ocultação dos detalhes de serialização/desserialização de dados de conta do processamento principal de instruções do seu programa. Assim, em vez de colocar todos os registros de serialização/desserialização no código de processamento do programa, ele encapsula os detalhes por trás de (3) funções:
unpack_unchecked- Permite que você desserialize uma conta sem verificar se ela foi inicializada. Isso é útil quando você está realmente processando a função de inicialização (índice de variante 0)unpack- Chama a sua implementação Pack deunpack_from_slicee verifica se a conta foi inicializadapack- Chama a sua implementação Pack depack_into_slice
Aqui está a implementação do trait Pack para o nosso programa de exemplo. Isso é seguido com o processamento real dos dados da conta usando o Borsh.
//! @brief account_state manages account data
use crate::error::SampleError;
use sol_template_shared::ACCOUNT_STATE_SPACE;
use solana_program::{
entrypoint::ProgramResult,
program_error::ProgramError,
program_pack::{IsInitialized, Pack, Sealed},
};
use std::collections::BTreeMap;
/// Maintains global accumulator
#[derive(Debug, Default, PartialEq)]
pub struct ProgramAccountState {
is_initialized: bool,
btree_storage: BTreeMap<String, String>,
}
impl ProgramAccountState {
/// Returns indicator if this account has been initialized
pub fn set_initialized(&mut self) {
self.is_initialized = true;
}
/// Adds a new key/value pair to the account
pub fn add(&mut self, key: String, value: String) -> ProgramResult {
match self.btree_storage.contains_key(&key) {
true => Err(SampleError::KeyAlreadyExists.into()),
false => {
self.btree_storage.insert(key, value);
Ok(())
}
}
}
/// Removes a key from account and returns the keys value
pub fn remove(&mut self, key: &str) -> Result<String, SampleError> {
match self.btree_storage.contains_key(key) {
true => Ok(self.btree_storage.remove(key).unwrap()),
false => Err(SampleError::KeyNotFoundInAccount),
}
}
}
impl Sealed for ProgramAccountState {}
// Pack expects the implementation to satisfy whether the
// account is initialzed.
impl IsInitialized for ProgramAccountState {
fn is_initialized(&self) -> bool {
self.is_initialized
}
}
impl Pack for ProgramAccountState {
const LEN: usize = ACCOUNT_STATE_SPACE;
/// Store 'state' of account to its data area
fn pack_into_slice(&self, dst: &mut [u8]) {
sol_template_shared::pack_into_slice(self.is_initialized, &self.btree_storage, dst);
}
/// Retrieve 'state' of account from account data area
fn unpack_from_slice(src: &[u8]) -> Result<Self, ProgramError> {
match sol_template_shared::unpack_from_slice(src) {
Ok((is_initialized, btree_map)) => Ok(ProgramAccountState {
is_initialized,
btree_storage: btree_map,
}),
Err(_) => Err(ProgramError::InvalidAccountData),
}
}
}
Serialização/Desserialização
Para completar a serialização e desserialização subjacente:
sol_template_shared::pack_into_slice- Onde ocorre a serialização realsol_template_shared::unpack_from_slice- Onde ocorre a desserialização real
Observação: no código a seguir temos uma partição u32 (4 bytes) no layout de dados para BTREE_LENGTH que precede o BTREE_STORAGE. Isso ocorre porque, durante a desserialização, o Borsh verifica se o comprimento da fatia que está sendo desserializada corresponde à quantidade de dados lidos antes de realmente recompor o objeto de destino. A abordagem demonstrada abaixo primeiro lê o BTREE_LENGTH para obter o tamanho da fatia (slice) a ser retirada do ponteiro BTREE_STORAGE.
use {
arrayref::*,
borsh::{BorshDeserialize, BorshSerialize},
solana_program::program_memory::sol_memcpy,
std::{collections::BTreeMap, error::Error},
};
/// Initialization flag size for account state
pub const INITIALIZED_BYTES: usize = 1;
/// Storage for the serialized size of the BTreeMap control
pub const BTREE_LENGTH: usize = 4;
/// Storage for the serialized BTreeMap container
pub const BTREE_STORAGE: usize = 1019;
/// Sum of all account state lengths
pub const ACCOUNT_STATE_SPACE: usize = INITIALIZED_BYTES + BTREE_LENGTH + BTREE_STORAGE;
/// Packs the initialized flag and data content into destination slice
#[allow(clippy::ptr_offset_with_cast)]
pub fn pack_into_slice(
is_initialized: bool,
btree_storage: &BTreeMap<String, String>,
dst: &mut [u8],
) {
let dst = array_mut_ref![dst, 0, ACCOUNT_STATE_SPACE];
// Setup pointers to key areas of account state data
let (is_initialized_dst, data_len_dst, data_dst) =
mut_array_refs![dst, INITIALIZED_BYTES, BTREE_LENGTH, BTREE_STORAGE];
// Set the initialized flag
is_initialized_dst[0] = is_initialized as u8;
// Store the core data length and serialized content
let keyval_store_data = btree_storage.try_to_vec().unwrap();
let data_len = keyval_store_data.len();
if data_len < BTREE_STORAGE {
data_len_dst[..].copy_from_slice(&(data_len as u32).to_le_bytes());
sol_memcpy(data_dst, &keyval_store_data, data_len);
} else {
panic!();
}
}
/// Unpacks the data from slice and return the initialized flag and data content
#[allow(clippy::ptr_offset_with_cast)]
pub fn unpack_from_slice(src: &[u8]) -> Result<(bool, BTreeMap<String, String>), Box<dyn Error>> {
let src = array_ref![src, 0, ACCOUNT_STATE_SPACE];
// Setup pointers to key areas of account state data
let (is_initialized_src, data_len_src, data_src) =
array_refs![src, INITIALIZED_BYTES, BTREE_LENGTH, BTREE_STORAGE];
let is_initialized = match is_initialized_src {
[0] => false,
[1] => true,
_ => {
return Err(Box::<dyn Error>::from(format!(
"unrecognized initialization flag \"{:?}\". in account",
is_initialized_src
)))
}
};
// Get current size of content in data area
let data_len = u32::from_le_bytes(*data_len_src) as usize;
// If emptry, create a default
if data_len == 0 {
Ok((is_initialized, BTreeMap::<String, String>::new()))
} else {
let data_dser = BTreeMap::<String, String>::try_from_slice(&data_src[0..data_len]).unwrap();
Ok((is_initialized, data_dser))
}
}
Utilização
A seguir, tudo se junta e demonstra como o programa interage com o ProgramAccountState, que encapsula a flag de inicialização, bem como o BTreeMap subjacente para nossos pares de chave/valor.
Primeiro, quando queremos inicializar uma nova conta:
/// Initialize a new program account, which is the first in AccountInfo array
fn initialize_account(accounts: &[AccountInfo]) -> ProgramResult {
msg!("Initialize account");
let account_info_iter = &mut accounts.iter();
let program_account = next_account_info(account_info_iter)?;
let mut account_data = program_account.data.borrow_mut();
// Here we use unpack_unchecked as we have yet to initialize
// Had we tried to use unpack it would fail because, well, chicken and egg
let mut account_state = ProgramAccountState::unpack_unchecked(&account_data)?;
// We double check that we haven't already initialized this accounts data
// more than once. If we are good, we set the initialized flag
if account_state.is_initialized() {
return Err(SampleError::AlreadyInitializedState.into());
} else {
account_state.set_initialized();
}
// Finally, we store back to the accounts space
ProgramAccountState::pack(account_state, &mut account_data).unwrap();
Ok(())
}
Agora podemos operar em nossas outras instruções como a seguinte demonstra a criação de um novo par chave-valor que demonstramos acima ao enviar instruções de um cliente:
/// Mint a key/pair to the programs account, which is the first in accounts
fn mint_keypair_to_account(accounts: &[AccountInfo], key: String, value: String) -> ProgramResult {
msg!("Mint to account");
let account_info_iter = &mut accounts.iter();
let program_account = next_account_info(account_info_iter)?;
let mut account_data = program_account.data.borrow_mut();
// Unpacking an uninitialized account state will fail
let mut account_state = ProgramAccountState::unpack(&account_data)?;
// Add the key value pair to the underlying BTreeMap
account_state.add(key, value)?;
// Finally, serialize back to the accounts data
ProgramAccountState::pack(account_state, &mut account_data)?;
Ok(())
}
Como desserializar dados da conta no cliente
Os clientes podem chamar a Solana para buscar contas de propriedade do programa, em que o bloco de dados serializados é parte do retorno. A desserialização requer conhecer o layout do bloco de dados.
O layout dos dados da conta foi descrito Aqui
import { serialize, deserialize, deserializeUnchecked } from "borsh";
import { Buffer } from "buffer";
import {
Keypair,
AccountMeta,
Connection,
LAMPORTS_PER_SOL,
PublicKey,
SystemProgram,
Transaction,
TransactionInstruction,
sendAndConfirmTransaction,
} from "@solana/web3.js";
// Flexible class that takes properties and imbues them
// to the object instance
class Assignable {
constructor(properties) {
Object.keys(properties).map((key) => {
return (this[key] = properties[key]);
});
}
}
export class AccoundData extends Assignable {}
const dataSchema = new Map([
[
AccoundData,
{
kind: "struct",
fields: [
["initialized", "u8"],
["tree_length", "u32"],
["map", { kind: "map", key: "string", value: "string" }],
],
},
],
]);
/**
* Fetch program account data
* @param {Connection} connection - Solana RPC connection
* @param {PublicKey} account - Public key for account whose data we want
* @return {Promise<AccoundData>} - Keypair
*/
export async function getAccountData(
connection: Connection,
account: PublicKey
): Promise<AccoundData> {
let nameAccount = await connection.getAccountInfo(account, "processed");
return deserializeUnchecked(dataSchema, AccoundData, nameAccount.data);
}
from borsh_construct import CStruct, U8, U32, HashMap, String
from solana.rpc.commitment import Confirmed
from solders.pubkey import Pubkey
from solana.rpc.api import Client
# Schema to deserialize program's account data
account_schema = CStruct(
"initialized" / U8,
"map_length" / U32,
"map" / HashMap(String, String)
)
def get_account_info(client: Client, account_pk: Pubkey):
"""Fetch account information from RPC, parse out the data and deserialize"""
res = client.get_account_info(account_pk, Confirmed, encoding='base64')
return account_schema.parse(res.value.data)
# Results in or similar
# => Container:
# => initialized = 1
# => map_length = 109
# => map = {'Happy': 'New Year!', 'newKey': 'A new value',
# => 'python key': 'python value', 'ts key': 'ts first value'}
use {
arrayref::*,
borsh::{BorshDeserialize, BorshSerialize},
std::{collections::BTreeMap, error::Error},
};
#[allow(clippy::ptr_offset_with_cast)]
pub fn unpack_from_slice(src: &[u8]) -> Result<(bool, BTreeMap<String, String>), Box<dyn Error>> {
let src = array_ref![src, 0, ACCOUNT_STATE_SPACE];
// Setup pointers to key areas of account state data
let (is_initialized_src, data_len_src, data_src) =
array_refs![src, INITIALIZED_BYTES, BTREE_LENGTH, BTREE_STORAGE];
let is_initialized = match is_initialized_src {
[0] => false,
[1] => true,
_ => {
return Err(Box::<dyn Error>::from(format!(
"unrecognized initialization flag \"{:?}\". in account",
is_initialized_src
)))
}
};
// Get current size of content in data area
let data_len = u32::from_le_bytes(*data_len_src) as usize;
// If emptry, create a default
if data_len == 0 {
Ok((is_initialized, BTreeMap::<String, String>::new()))
} else {
let data_dser = BTreeMap::<String, String>::try_from_slice(&data_src[0..data_len]).unwrap();
Ok((is_initialized, data_dser))
}
}
Mapeamentos comuns da Solana em TypeScript/JavaScript
A Especificação do Borsh contêm a maioria dos mapeamentos para tipos de dados primitivos e compostos.
A chave para TS/JS e Python é criar um esquema Borsh com uma definição adequada para que a serialização e desserialização possam gerar ou percorrer as respectivas entradas.
Aqui demonstramos a serialização de tipos primitivos (números, strings) e tipos compostos (array de tamanho fixo, mapeamento) primeiro em Typescript, depois em Python e, em seguida, a desserialização equivalente no lado do Rust:
#!/usr/bin/env node
import { serialize, deserialize, deserializeUnchecked } from "borsh";
import { Buffer } from "buffer";
import { expect } from "chai";
import { PublicKey, Struct } from "@solana/web3.js";
/**
* Primitive extends the Struct type from Solana Library
* for convenience of dynamic property setting
* @extends {Struct} Solana JS Struct class
*/
class Primitive extends Struct {
constructor(properties) {
super(properties);
}
}
/**
* Entry point for script *
*/
async function entry() {
// Emulate BTreeMap
let map = new Map();
map.set("cookbook", "recipe");
map.set("recipe", "ingredient");
// Setup a Primitive for all basic and a few
// compound types
const value = new Primitive({
U8: 255,
U16: 65535,
U32: 4294967295,
FIXED_STRING_ARRAY: ["hello", "world"],
FIXED_U8_ARRAY: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5],
MAP_STRING_STRING: map,
});
// Define our schema
const schema = new Map([
[
Primitive,
{
kind: "struct",
fields: [
["U8", "u8"],
["U16", "u16"],
["U32", "u32"],
["FIXED_STRING_ARRAY", ["string", 2]],
["FIXED_U8_ARRAY", ["u8", 5]],
[
"MAP_STRING_STRING",
{ kind: "map", key: "string", value: "string" },
],
],
},
],
]);
console.log("Value = ", value);
// Serialize then deserialize
const dser = Buffer.from(serialize(schema, value));
console.log(dser);
const newValue = deserialize(schema, Primitive, dser);
// Viola!
console.log("New value = ", newValue);
console.log("Fixed string array = ", newValue["FIXED_STRING_ARRAY"]);
console.log("Fixed u8 array = ", newValue["FIXED_U8_ARRAY"]);
console.log("Map = ", newValue["MAP_STRING_STRING"]);
}
entry();
from borsh_construct import U8, U16, U32, String, HashMap
# Schema to deserialize various types
primitive_schema = CStruct(
"U8" / U8,
"U16" / U16,
"U32" / U32,
"FIXED_STRING_ARRAY" / String[2],
"FIXED_U8_ARRAY" / U8[5],
"MAP_STRING_STRING" / HashMap(String, String)
)
def common():
mapping = {"cookbook": "recipe", "recipe": "ingredient"}
# Serialize
dser = primitive_schema.build({
'U8': 255,
'U16': 65535,
'U32': 4294967295,
"FIXED_STRING_ARRAY": ['hello', 'world'],
"FIXED_U8_ARRAY": [1, 2, 3, 4, 5],
"MAP_STRING_STRING": mapping})
print(dser)
# => b'\xff\xff\xff\xff\xff\xff\xff\x05\x00\x00\x00hello\x05\x00\x00\x00world\x01\x02\x03\x04\x05\x02\x00\x00\x00\x08\x00\x00\x00cookbook\x06\x00\x00\x00recipe\x06\x00\x00\x00recipe\n\x00\x00\x00ingredient'
# Deserialize
new_value = primitive_schema.parse(dser)
# Viola
print(new_value)
# => Container:
# => U8 = 255
# => U16 = 65535
# => U32 = 4294967295
# => FIXED_STRING_ARRAY = ListContainer:
# => hello
# => world
# => FIXED_U8_ARRAY = ListContainer:
# => 1
# => 2
# => 3
# => 4
# => 5
# => MAP_STRING_STRING = {'cookbook': 'recipe', 'recipe': 'ingredient'}
fn main() {}
#[cfg(test)]
mod tests {
use borsh::{BorshDeserialize, BorshSerialize};
use std::collections::BTreeMap;
#[test]
fn primitives() {
let prim = [
255u8, 255, 255, 255, 255, 255, 255, 5, 0, 0, 0, 104, 101, 108, 108, 111, 5, 0, 0, 0,
119, 111, 114, 108, 100, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 2, 0, 0, 0, 8, 0, 0, 0, 99, 111, 111, 107, 98,
111, 111, 107, 6, 0, 0, 0, 114, 101, 99, 105, 112, 101, 6, 0, 0, 0, 114, 101, 99, 105,
112, 101, 10, 0, 0, 0, 105, 110, 103, 114, 101, 100, 105, 101, 110, 116,
];
#[derive(BorshDeserialize, BorshSerialize, Debug)]
struct Primitive(
u8,
u16,
u32,
String,
String,
[u8; 5],
BTreeMap<String, String>,
);
let x = Primitive::try_from_slice(&prim).unwrap();
println!("{:?}", x);
}
}
Construções avançadas
Mostramos como criar cargas úteis (payloads) simples em exemplos anteriores. Às vezes, a Solana apresenta alguns tipos mais complexos. Esta seção demonstrará a correspondência adequada entre TS/JS e Rust para lidar com esses tipos.
COption
#!/usr/bin/env node
import { serialize, deserialize, deserializeUnchecked } from "borsh";
import { Buffer } from "buffer";
import { PublicKey, Struct } from "@solana/web3.js";
/**
* COption is meant to mirror the
* `solana_program::options::COption`
*
* This type stores a u32 flag (0 | 1) indicating
* the presence or not of a underlying PublicKey
*
* Similar to a Rust Option
* @extends {Struct} Solana JS Struct class
* @implements {encode}
*/
class COption extends Struct {
constructor(properties) {
super(properties);
}
/**
* Creates a COption from a PublicKey
* @param {PublicKey?} akey
* @returns {COption} COption
*/
static fromPublicKey(akey?: PublicKey): COption {
if (akey == undefined) {
return new COption({
noneOrSome: 0,
pubKeyBuffer: new Uint8Array(32),
});
} else {
return new COption({
noneOrSome: 1,
pubKeyBuffer: akey.toBytes(),
});
}
}
/**
* @returns {Buffer} Serialized COption (this)
*/
encode(): Buffer {
return Buffer.from(serialize(COPTIONSCHEMA, this));
}
/**
* Safe deserializes a borsh serialized buffer to a COption
* @param {Buffer} data - Buffer containing borsh serialized data
* @returns {COption} COption object
*/
static decode(data): COption {
return deserialize(COPTIONSCHEMA, this, data);
}
/**
* Unsafe deserializes a borsh serialized buffer to a COption
* @param {Buffer} data - Buffer containing borsh serialized data
* @returns {COption} COption object
*/
static decodeUnchecked(data): COption {
return deserializeUnchecked(COPTIONSCHEMA, this, data);
}
}
/**
* Defines the layout of the COption object
* for serializing/deserializing
* @type {Map}
*/
const COPTIONSCHEMA = new Map([
[
COption,
{
kind: "struct",
fields: [
["noneOrSome", "u32"],
["pubKeyBuffer", [32]],
],
},
],
]);
/**
* Entry point for script *
*/
async function entry(indata?: PublicKey) {
// If we get a PublicKey
if (indata) {
// Construct COption instance
const coption = COption.fromPublicKey(indata);
console.log("Testing COption with " + indata.toBase58());
// Serialize it
let copt_ser = coption.encode();
console.log("copt_ser ", copt_ser);
// Deserialize it
const tdone = COption.decode(copt_ser);
console.log(tdone);
// Validate contains PublicKey
if (tdone["noneOrSome"] == 1) {
console.log("pubkey: " + new PublicKey(tdone["pubKeyBuffer"]).toBase58());
}
/*
Output:
Testing COption with A94wMjV54C8f8wn7zL8TxNCdNiGoq7XSN7vWGrtd4vwU
copt_ser Buffer(36) [1, 0, 0, 0, 135, 202, 71, 214, 68, 105, 98, 176, 211, 130, 105, 2, 55, 187, 86, 186, 109, 176, 80, 208, 77, 100, 221, 101, 20, 203, 149, 166, 96, 171, 119, 35, buffer: ArrayBuffer(8192), byteLength: 36, byteOffset: 1064, length: 36]
COption {noneOrSome: 1, pubKeyBuffer: Uint8Array(32)}
pubkey: A94wMjV54C8f8wn7zL8TxNCdNiGoq7XSN7vWGrtd4vwU
*/
} else {
console.log("Testing COption with null");
// Construct COption instance
const coption = COption.fromPublicKey();
// Serialize it
const copt_ser = coption.encode();
console.log(copt_ser);
// Deserialize it
const tdone1 = COption.decode(copt_ser);
console.log(tdone1);
// Validate does NOT contains PublicKey
if (tdone1["noneOrSome"] == 1) {
throw Error("Expected no public key");
} else console.log("pubkey: null");
/*
Output:
Testing COption with null
Buffer(36)[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, buffer: ArrayBuffer(8192), byteLength: 36, byteOffset: 2272, length: 36]
COption { noneOrSome: 0, pubKeyBuffer: Uint8Array(32) }
pubkey: null
*/
}
}
// Test with PublicKey
entry(new PublicKey("A94wMjV54C8f8wn7zL8TxNCdNiGoq7XSN7vWGrtd4vwU"));
console.log("");
// Test without PublicKey
entry();
fn main() {}
#[cfg(test)]
mod tests {
use arrayref::{array_ref, array_refs};
use solana_program::{program_option::COption, pubkey::Pubkey};
/// Emulate how COption is 'unpacked'
fn deser_option(data: &[u8]) -> COption<Pubkey> {
// Map the data block
let ain = array_ref![data, 0, 36];
let (base, key) = array_refs![ain, 4, 32];
// Get the SOME or NONE u32
let nos = u32::from_le_bytes(*base);
// Construct the COption accordingly
let opt: COption<Pubkey> = if nos == 0 {
COption::None
} else {
COption::Some(Pubkey::new_from_array(*key))
};
opt
}
#[test]
fn btest() {
// From Typescript with borsh'ing
let copt = [
1u8, 0, 0, 0, 135, 202, 71, 214, 68, 105, 98, 176, 211, 130, 105, 2, 55, 187, 86, 186,
109, 176, 80, 208, 77, 100, 221, 101, 20, 203, 149, 166, 96, 171, 119, 35,
];
// Emulate COption deserialization
let coption = deser_option(&copt);
if coption.is_some() {
println!("{:?}", coption.expect("Uh-oh"));
}
// As a Borsh Struct
#[derive(BorshDeserialize, BorshSerialize, Debug)]
struct TOption(u32, [u8; 32]);
let toption = TOption::try_from_slice(&copt).unwrap();
let pkey = Pubkey::new_from_array(toption.1);
println!("Some = {:?} Pubkey = {:?}", toption.0, pkey);
}
}